rev 5/1/25
Chloroform production and use
Main properties
Molecular Formula CHCl3
Molecular Weight 119.37 g/molOdor Pleasant, etheric, nonirritating
Boiling Point 61.12 °C
Melting Point -82.3 °F -63.47 °C
Density (at 20 °C): 1.48 g/ml
Synonyms
67-66-3 Chloroform Chloroforme (French)
Formyl trichloride Methane trichloride Methenyl chloride
Methenyl trichloride Methyl trichloride NCI-C02686
Pure chloroform is light sensitive and reagent grade chloroform usually contains 0.75% ethanol as stabilizer
CHLOROFORM PRODUCTION
Chlorination
of methane is well known with many patents taken by various
corporations since 1879 .The reaction which very exothermic is done in continuous
and give a mixture of diffferents chloroalcanes CHCl3,
CH2Cl2,CHCl3,CCl4.....which are separated by distillation .The reaction
is carried out between 200 et 500° c under pressure with short reaction
time (in the second range) .
The
reaction can also be done in liquid phase with the help of UV light
(Photochlorination) .In this case conditions are generally milder e.g. temp
50°c pressure few bars.
It is also possible to
get chloroform by dechloration of carbon tetrachloride as
mentioned in patent
EP0460138B1 Published 1995-02-15
As the market of chloroalacanes is changing over the time the processes have to be flexible to fit production to the market
Here are some examples taken from a very rich patent litterature .More details here
Vapor Chlorination of methane
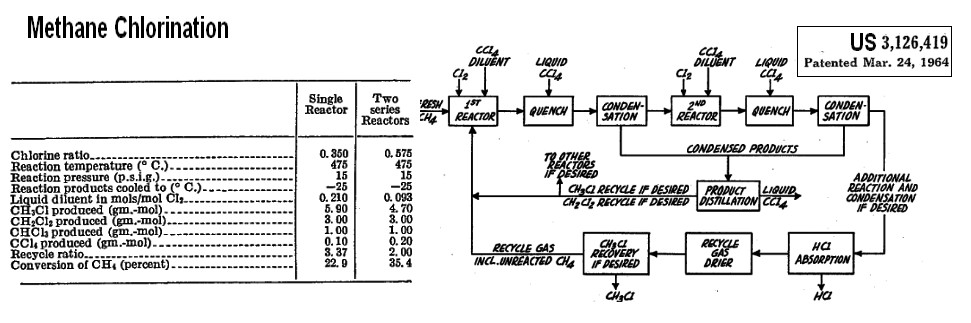
US 3,126,419 CHLORINATION OF METHANE assignors to Stauffer Chemical Filed Sept. 26, 1960, Ser. No. 58,367
This
invention relates in general to a process for the partial chlorination
of methane and in particular to a process for maximum production of
methylene chloride
and/or to chloroform via the chlorination of methane.
Chlorination of methyl chloride/methylene dichloride
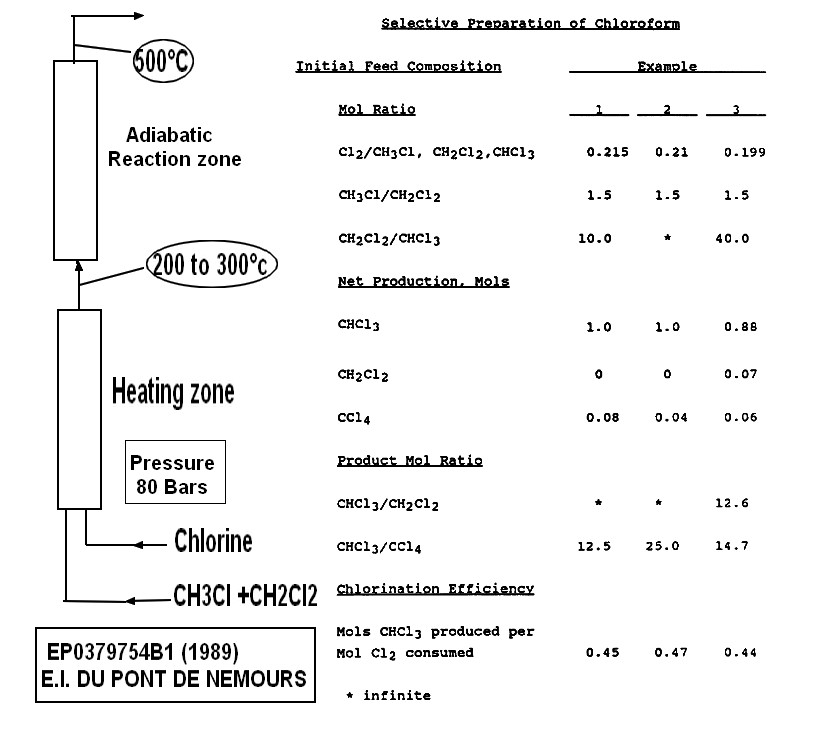
EP0379754B1 E.I. Du Pont De Nemours Priority
1987-11-10 • Filed 1989-01-24 • Granted 1994-03-23 • Published
1994-03-23
The
chlorinated methanes (methyl chloride, methylene chloride, chloroform
and carbon tetrachloride) are well-known articles of commerce and are
generally prepared by chlorination of an underchlorinated raw material.
As the demand for the individual members of the series varies from time
to time, it is desirable to be able to control their production
accordingly.
At present (1987) the demand for chloroform
is high, that for methylene chloride and carbon tetrachloride is low.
The existing chlorination processes, however, are not entirely
satisfactory for producing chloroform to the substantial exclusion of
the other polychloromethanes. For example, the direct chlorination of
methane for this purpose (described in SRI #126, C₁ Chlorinated
Hydrocarbons, published August 1978, pages 49 to 96) is difficult to
control and expensive to operate because of the necessity of recycling
large amounts of methane, methyl chloride and methylene chloride. It
also tends to produce undesirably high ratios of carbon tetrachloride
to chloroform, which constitutes a cost penalty in view of the
relatively low demand for the tetrachloride.
The production of
methyl chloride is readily controlled by utilizing the reaction of
hydrogen chloride with methanol, and for this reason it is an
attractive starting material for the higher chlorinated methanes.
CH3Cl + CH2Cl2 + Cl2 -------> CHCl3 +CCl4 Pressure 80 bars temp 200 to 500°c
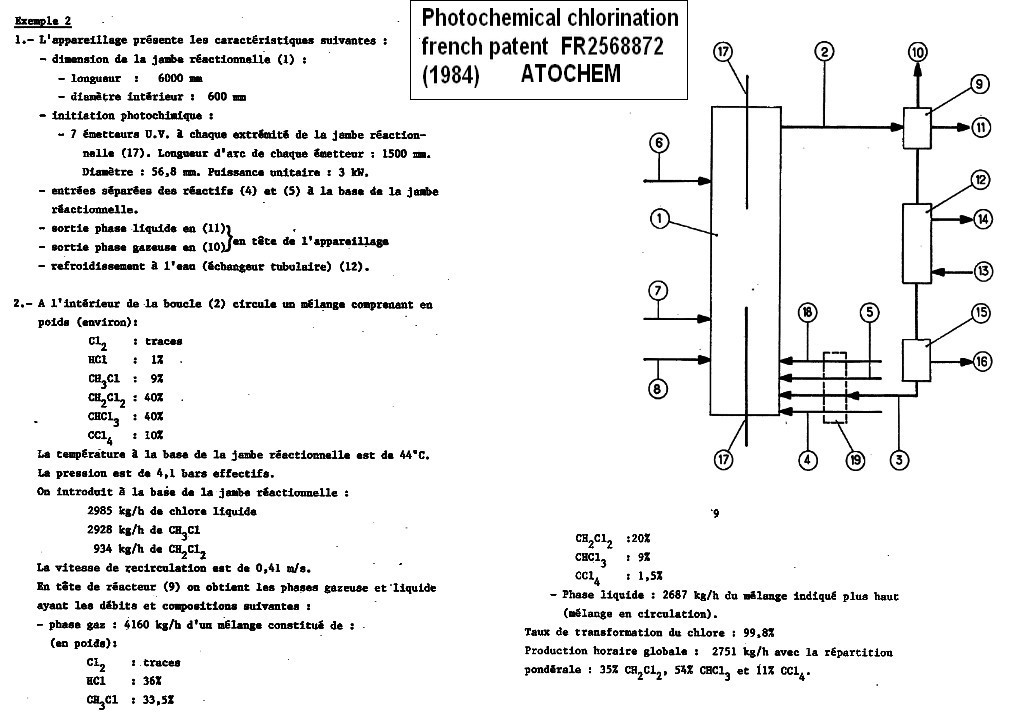
PhotoChlorination of methyl chloride/methylene dichloride
FR2568872B1 * 1984-04-27 1986-11-28
Atochem CONTINUOUS PROCESS OF RADICAL CHLORINATION OF
CHLOROALKANES
The chlorination of a mixture of methyl
chloride/methylen chloride can be done by activation of chlorine with
UV lamps (photochlorination) in liquid phase .In this case typical
working condition are : temperature 44°c , pressure 4 bars
.Chloroform is the main product with small amounts de CCl4
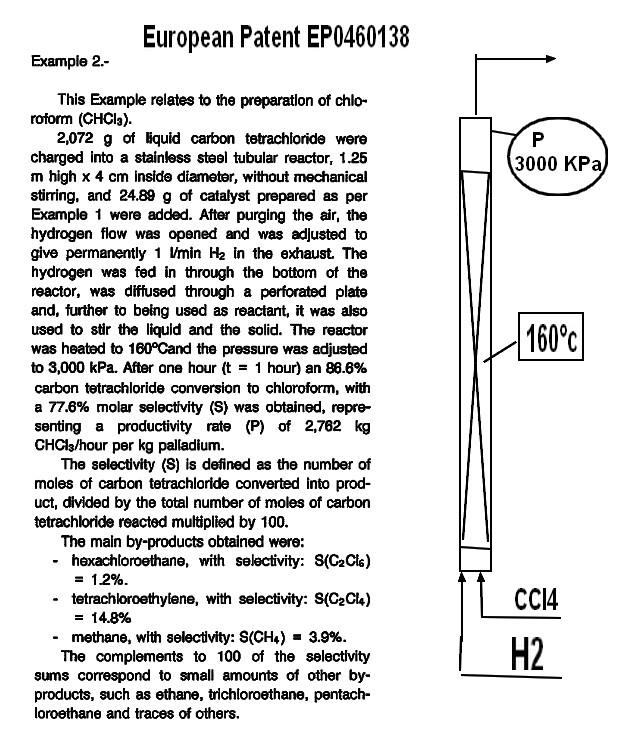
CHCl3 by catalytical hydrogenation of CCl4
EP0460138 Priority 1989-12-22 • Filed 1990-12-13 • Granted 1995-02-15 • Published 1995-02-15
CCl4 + H2 ------> CHCl3 + HCl
Catalyst Pd/Carbon temp 160°C pressure 3000 KPa
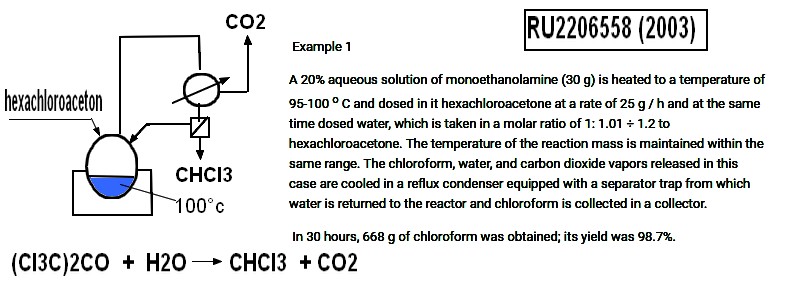
CHCl3 from hexachloroacetone
Russia Patent RU2206558C1 2003-06-20 Publication of RU2206558C1
The
method of producing chloroform by hydrolysis of hexachloroacetone at
elevated temperature, characterized in that hexachloroacetone is
hydrolyzed with water in the presence of ethanolamines as a catalyst at
95-150 o With simultaneous distillation of the reaction product -
chloroform.
Hexachloroacetone
can be obtained by action of chlorine on ispropanol or better from
acetone in very good yield (>95%) , catalysis by pyridine as depicted in China patent
CN109942392A (2022-01-21)
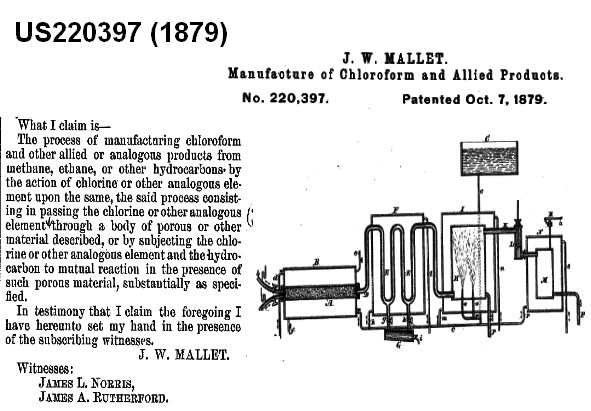
Vintage processes
Chlorination of methane (1879)
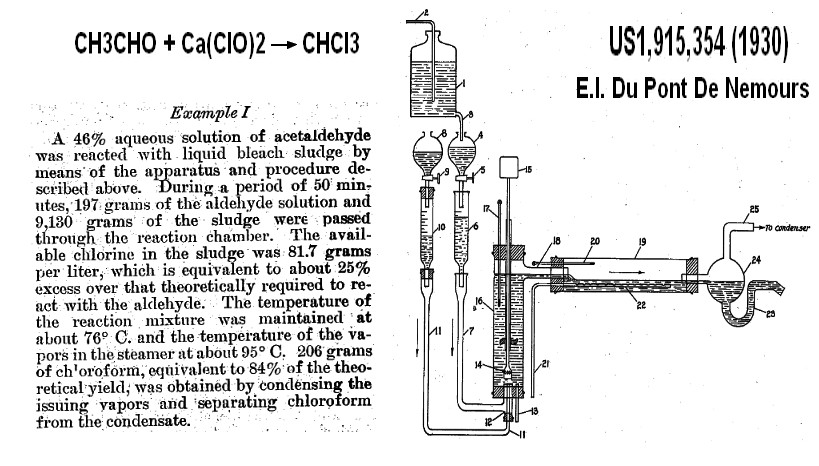
decarboxylation trichloroacetic Calcium salt(1928)

Chlorination of carbonyl product
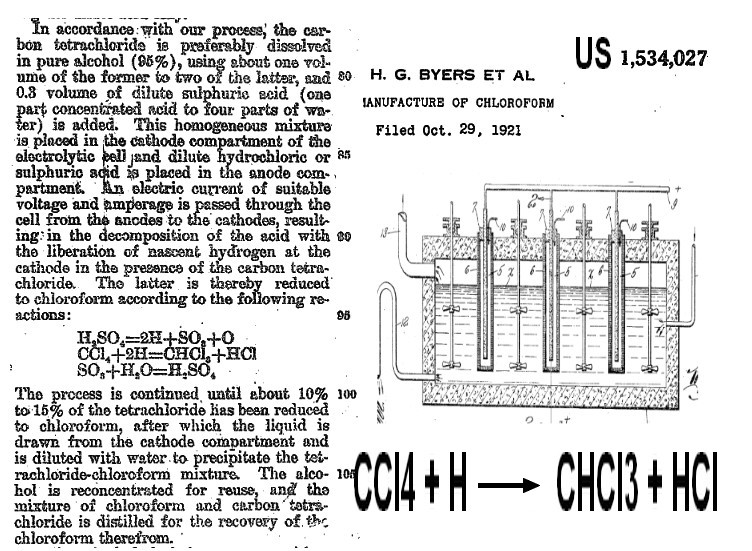
Electro Reduction of CCl4
Elctroreduction of carbone tetra chloride in mixture CCl4/EtOH/H2SO4 (US1534027 (1921)
Chemical reduction of CCl4
US2104703A Dow Chemical Co Priority 1936-02-13 • Filed 1936-02-13 • Granted 1938-01-04 • Published 1938-01-04
Patented
Jan. 4, 1938 UNHTED S'E'AS Arm FFlE METHOD FOR. THE MANUFACTURE OF
CHLOROFORM No Drawing. Application February 13, 1936, Serial No. 63,734
9 Claims. This invention concerns an improved method of manufacturing
chloroform by reaction of carbon tetrachloride with iron and water.
2CCl4 + 2H2O + 2 Fe --->FeCl2 + Fe(OH)2 + 2CHCl3
Reaction catalysed by various Pb salt
CHLOROFORM USAGE
In terms of scale, the most important use of chloroform is to give monochlorodifluoromethane (HCFC-22 alias R-22),
CHCl3 + 2 HF → CHClF2 + 2 HCl
The reaction is conducted in the presence of a catalytical amount of mixed antimony halides.
Chlorodifluoromethane
, a colorless gas is better known as HCFC-22, or R-22, or CHClF2. It
was commonly used as a propellant and refrigerant. These applications
were phased out under the Montreal Protocol in developed countries in
2020 due to the compound's ozone depletion potential (ODP) and high
global warming potential (GWP), and in developing countries this
process will be completed by 2030.
R-22 still remain a
versatile intermediate in industrial organofluorine chemistry, e.g. as
a precursor to tetrafluoroethylene by pyrolysis (at 550–750 °C) ,
with difluorocarbene as an intermediate.
2 CHClF2 → C2F4 + 2 HCl
Polymerization
of tetrafluoroethylene produces polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymers
such as Teflon , Fluon and many others
Worldwide,
chloroform is also used in pesticide formulations, as a solvent for
lipids, rubber, alkaloids, waxes, gutta-percha, and resins, as a
cleaning agent, as a grain fumigant, in fire extinguishers, and in the
rubber industry.








