
 |
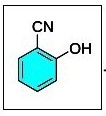
| 2 cyano phenol routes : detailed info : |
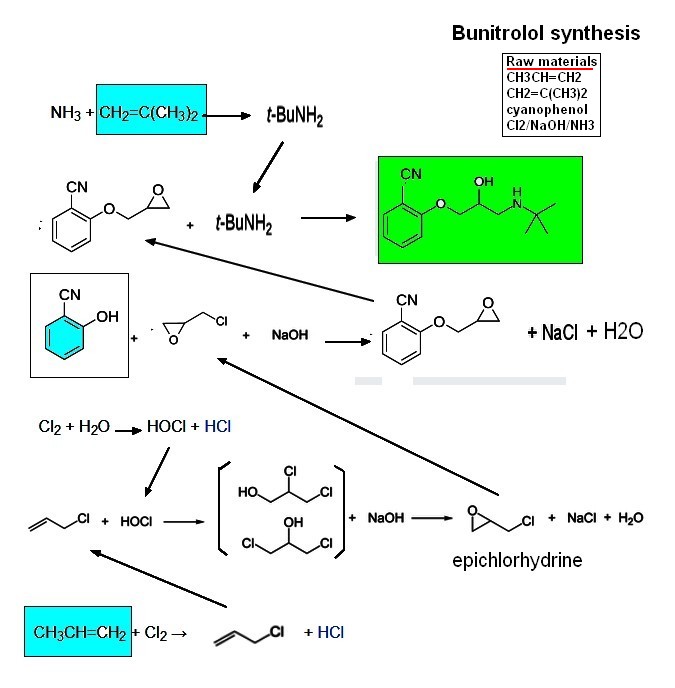 |
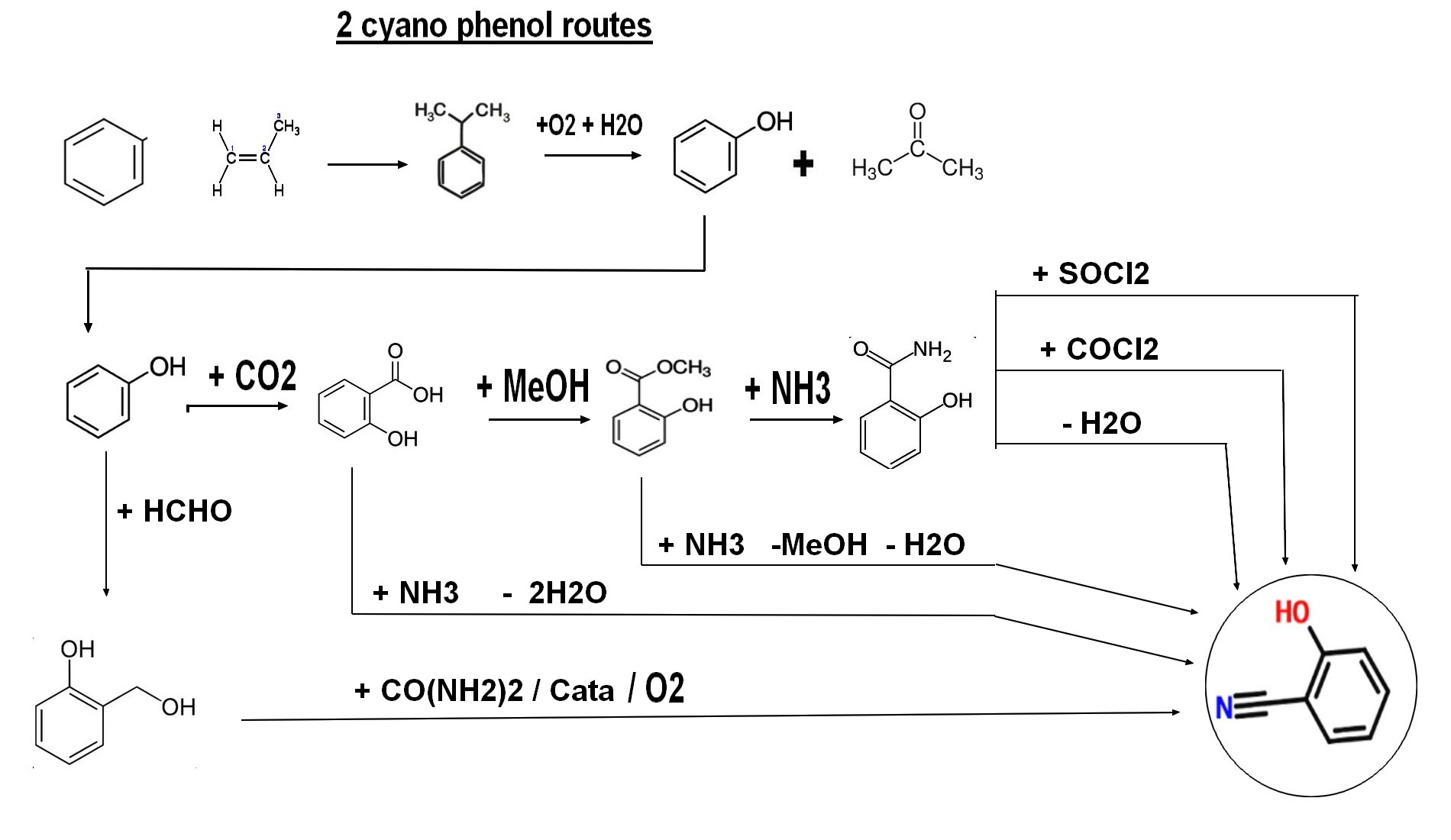
| bunitrolol: Bunitrolol is a beta-adrenergic antagonist, commonly known as a beta-blocker, used primarily in the treatment of coronary heart disease. It functions by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, which leads to a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, thereby reducing the heart's workload. Chemically, bunitrolol is identified by the molecular formula C₁₄H₂₀N₂O₂ and has a molecular weight of 248.32 g/mol. Its IUPAC name is 2-[3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]benzonitrile. Bunitrolol exhibits a higher affinity for beta-1 adrenergic receptors compared to beta-2 receptors and also possesses weak alpha-1 blocking activity. This selectivity contributes to its effectiveness in improving cardiac performance in patients with coronary artery disease. In clinical settings, bunitrolol has been administered intravenously at doses of 10 mg to patients with coronary artery disease. |
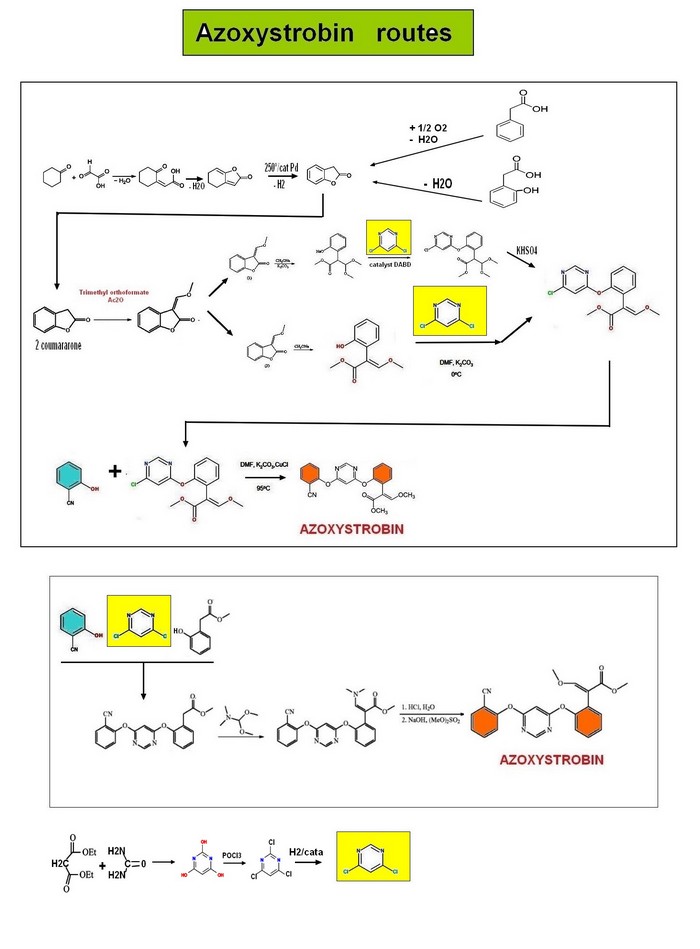 |
| azoxystrobin Chemical Properties:
Azoxystrobin is a broad-spectrum systemic fungicide widely used in agriculture to protect crops from various fungal diseases. It was first marketed in 1996 under the brand name Amistar and has since been registered in numerous countries for use on a variety of crops. Usage: Azoxystrobin is effective against a wide range of fungal pathogens, including those from the Ascomycota, Deuteromycota, and Basidiomycota groups, as well as oomycetes. It is registered for use on various crops such as wheat, barley, oats, rye, soybeans, cotton, rice, strawberries, peas, beans, onions, and many other vegetables. Its systemic properties allow it to move through plant tissue, providing protection to parts of the crop not directly treated. Formulations: Azoxystrobin is available in various formulations alone or with other fungicides to suit different application methods. One such formulation is Azoxy 2SC Select, a suspension concentrate that provides continuous protection to the whole plant for up to 28 days through a combination of foliar and root absorption. Environmental Impact: Azoxystrobin has a low potential for bioconcentration and poses moderate risks to fish, earthworms, and bees. However, it presents a high risk to aquatic crustaceans, so care must be taken to avoid runoff into water bodies. Its main degradation product, resulting from hydrolysis of its methyl ester, is also potentially harmful to aquatic environments. Azoxystrobin producers Azoxystrobin is a widely used fungicide developed by Syngenta, which markets it under brand names such as Amistar and Heritage. Other companies also produce and distribute azoxystrobin-based products:
|
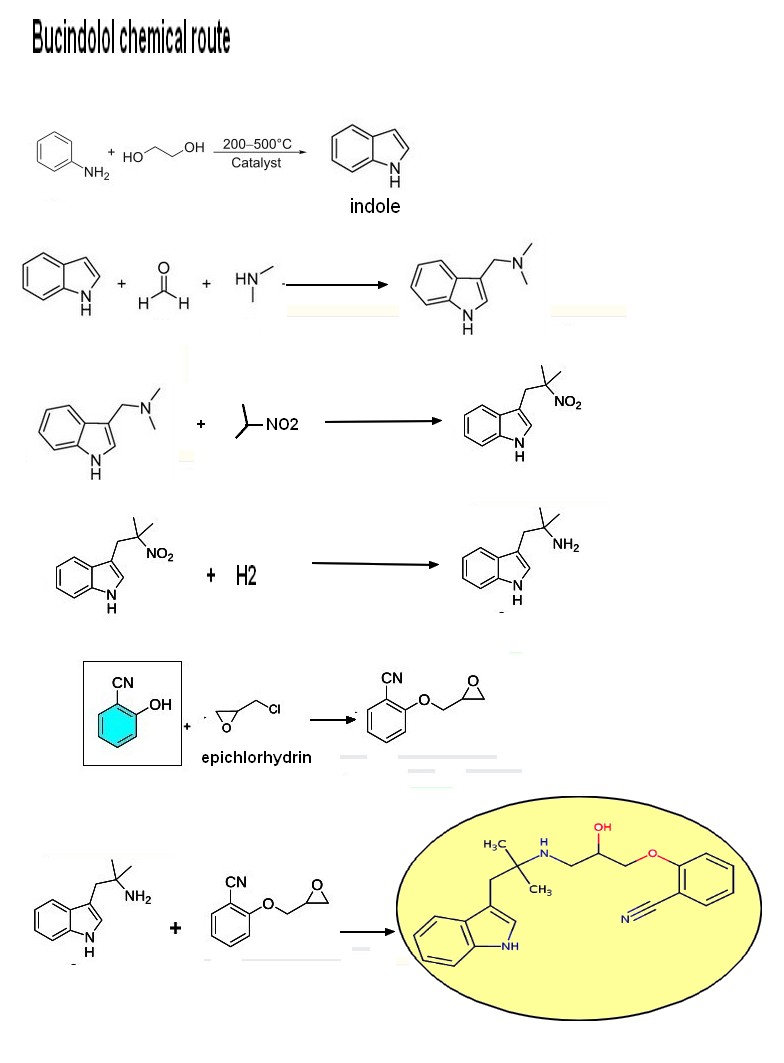 |
Bucindolol is a non-selective beta-blocker with mild intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) and vasodilatory properties. It has been studied primarily for its potential use in treating heart failure and hypertension, but its development has faced challenges due to mixed clinical trial results. Ongoing research focuses on its role in precision medicine, aiming to identify specific patient populations who might derive significant benefits based on their genetic makeup. |
epanolol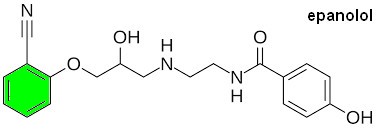 |
Epanolol is a cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist, commonly known as a beta-blocker, developed by Imperial Chemical Industries (now part of AstraZeneca now ). It is primarily used in the management of cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension and angina pectoris. Development Status: Despite its demonstrated efficacy, the development and registration of epanolol have been discontinued in several countries, including France, Germany, and Sweden. |