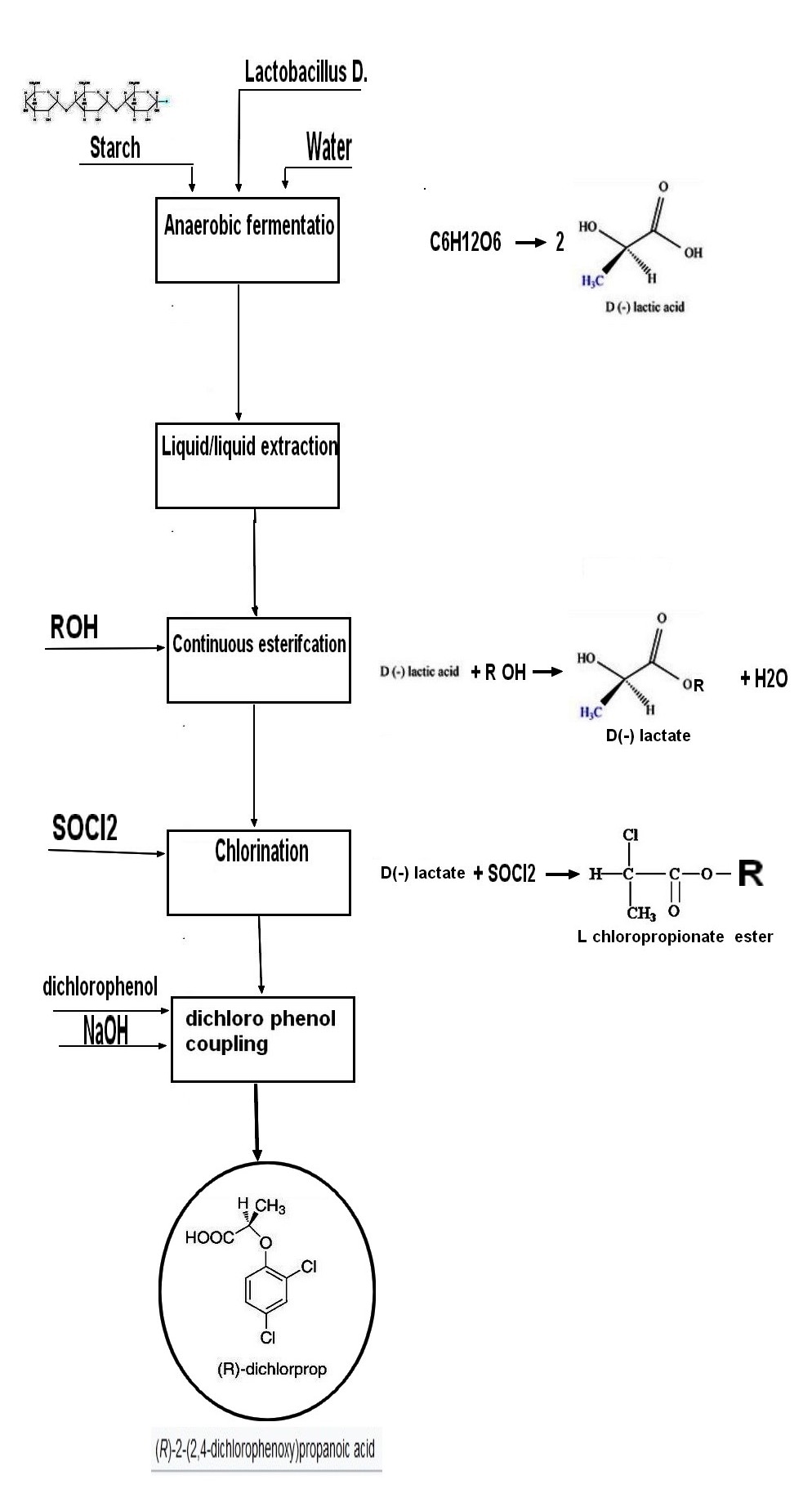
The fiirst step is making D Lactic acid by fermetnation of a sugar like hydrolyzed starch , dextose .The strain used is generally L Bacillus Delbruckii. .The chemical yield based on reaction
C6H12O6 ===> 2 CH3CH(OH)CO2H
is more than 90% , with an L/D isomer being kept below the 0.2% mark if the starting raw material was not contaminated before its use
The fermetation is done batchwise at a temperature around 120 °F and takes around 60 hours to complete (time can be reduced by increasing the amount of strain used in inoculum) .The rection is exothemic and the fermetors should be cooled by circulated chilled water in internal coils .Some basic agent has to be added during fermentation to keep pH in the specific zone depending on the strain used .Due to the high fermentation temperature the risk of contamination by bacteria or yeast is unlikely
EXTRACTION
The fermentation broth is acidified and extracted with a solvent or a mixture of solvent so as to extract lactic acid .After this step a solution of D lactic acid is obtained as a liquid having about 20 % of water in it .The operation is done in continuous and does not degrade the isomeric ratio D/L .
ESTERIFICATION
Esterification is done in continuous with various alccol depending on the need of final customer .The main side reaction is polycondensation of lactic acid on itself .The polymer is depolymerized and recycled to the esterification .The chemical yield is over 95% , the racemization kept under 0.3%.The esterification does not change the assymetric carbon configuration thanks to the catalytical acid used .
CHLORINATION
It is done batchwise using either thionyl chloride(SOCl2) or phosgene (COCl2).With thionyl chloride a small amount of catalyst is needed (generally pyridinium compound which has to be kept as low as possible to prevent racemization) .The reaction generate SO2 and HCl as by products .If phosgenation is prefered a solvent is necessary and must be collected and recycled .After reaction the configuration of assymetric carbon is inversed (passing from D config to L config) .The chemical yield is over 90% Using phosgene require generally a solvent like toluene or dichloromethane and also small amounts of tertiary base like pyridine or triethyl amine .As phosgene is more dangerous to handle thionyl chloride is often prefered even if the by products of the reaction are easier to get rid off (HCl + CO2) vs (SO2+HCl)
DICHLOROPHENOL COUPLING
Reaction is made by reaction of (L) Chloroprionate (Fisher rule) (also refered as (S) chloropropionate) on the dichloro phenate in a solvent .This step inverse the assymetric carbon which becomes (R) according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules .As the final product can be either acid form , salt form or ester form the solvent and the chemical treatment is adjusted accordingly ..In all cases NaCl or KCl is by producted
.