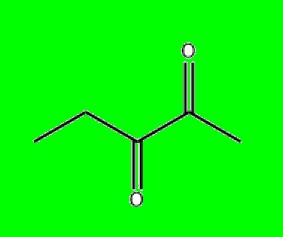
2,3-Pentanedione, also known as acetylpropionyl, is an organic
compound with the molecular formula C₅H₈O₂. It is a yellow to
green-yellow liquid characterized by a buttery odor.
2,3 pentanedione is a vicinal diketone (as diacetyl) which contribute importantly to the flavor and aroma of such diverse products as baked goods, fruits including citrus and red fruits, brewery products, meat, coffee, cocoa, dairy products, etc etc .It is also generated during cooking
Physical Properties:
Molecular Weight: 100.12 g/mol
Boiling Point: 230-234°F (110-112°C)
Freezing Point: -61.6°F (-52°C)
Flash Point: 66°F (19°C)
Uses:
As a Flavoring Agent 2,3-Pentanedione imparts buttery, cheesy, sweet, nutty, fruity, creamy, and caramel-like flavors. It occurs naturally in various foods, including butter, bread, milk, yogurt, chicken, meat, cocoa, coffee, potato chips, roasted almonds, pecans, beer, and wine. In the food industry, it is used to flavor products such as cookies, coffee, cereal, and chocolate. Additionally, it is found in nicotine-containing liquids for vaping and in flavored cigarettes, often as a substitute for diacetyl.
It is widely used as food additives ,its contents being variable always in th ppm range :
Sweet sauce 0.5 ppm
Alcoholic beverages 1 ppm
Meat products 5 ppm
Breakfast cereals 10 ppm
Hard candy 50 ppm
2,3-Pentanedione is also utilized as a starting material in the synthesis of various chemicals .
Health and Safety Considerations:
Exposure to 2,3-pentanedione has been associated with respiratory health concerns. Studies indicate that inhalation can lead to severe respiratory tract injury, including fibrosis and necrosis, similar to the effects observed with diacetyl exposure. Animal studies have shown that it can cause genetic changes in the brain and alter gene expression. Due to its potential pulmonary toxicity, there is concern regarding its use as a flavoring agent, particularly in occupational settings where inhalation exposure may occur.
2,3 Pentane dione synthesis
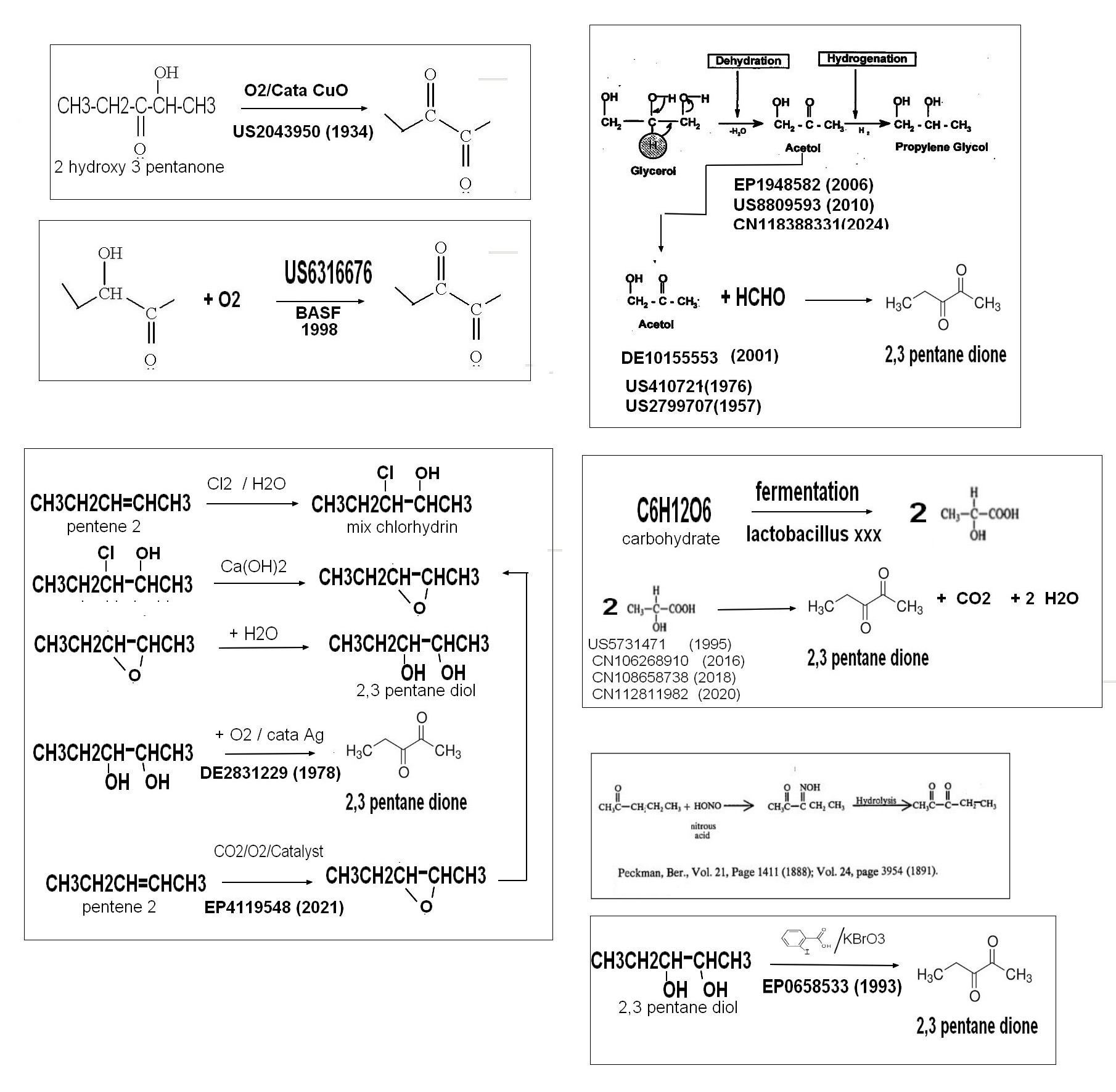
pentanedione can be synthesized starting from various products as outlined below .
The simplest route is the one starting from carbohydrates which give lactic acid by fermentation with a lactobacillus strain (chemical yield >95%) .The lactic acid reacts on itself with various catalyst (temperature range 200/350°c) to give 2,3 pentanone dione , the product being purified by distillation .This route is examplified in several patents (example US5731471.) or academic publications (one of the last one ) which are dealing about the best catalyst to run the reaction .
C6H12O6 ===================> 2 CH3CHOHCO2H
2 CH3CHOHCO2H =============>2,3 pentane dione + CO2 + 2 H2O
Another simple way to get 2,3 pentanone dione is starting from glycerol , a by product widely available from the biofuel industry ,by dehydration to get hydroxy aceton which is formylated to obtanin 2,3pentane dione .This route is covered by numerous patents
The third route is starting from pentene 2 to get 2,3 pentandiol (either by classical route HClO/Ca(OH)2/H2O or oxydataion+hydration) .The 2,3 petanediol is oxydized in 2,3 pentanedione using silver catalyst ,It should be noted that 2,3 pentanediol can also be dehydrogenetated in vapor phase using ZnO or Cu catalyst to give 2,3 pentandione .
2,3 pentandiol can be also oxydized by the iodo oxybenzoic acid (KBrO3+ 2 iodobenzoic acid ) to give 2,3 pentane dione , this route being patented in 1993
Some other synthesis are also possible for example by oxydation of 2 pentanone (first mentioned in 1888) or hydroxy pentanone (patented by several corporation)
more details here
2,3 pentanedione is a vicinal diketone (as diacetyl) which contribute importantly to the flavor and aroma of such diverse products as baked goods, fruits including citrus and red fruits, brewery products, meat, coffee, cocoa, dairy products, etc etc .It is also generated during cooking
Physical Properties:
Molecular Weight: 100.12 g/mol
Boiling Point: 230-234°F (110-112°C)
Freezing Point: -61.6°F (-52°C)
Flash Point: 66°F (19°C)
Uses:
As a Flavoring Agent 2,3-Pentanedione imparts buttery, cheesy, sweet, nutty, fruity, creamy, and caramel-like flavors. It occurs naturally in various foods, including butter, bread, milk, yogurt, chicken, meat, cocoa, coffee, potato chips, roasted almonds, pecans, beer, and wine. In the food industry, it is used to flavor products such as cookies, coffee, cereal, and chocolate. Additionally, it is found in nicotine-containing liquids for vaping and in flavored cigarettes, often as a substitute for diacetyl.
It is widely used as food additives ,its contents being variable always in th ppm range :
Sweet sauce 0.5 ppm
Alcoholic beverages 1 ppm
Meat products 5 ppm
Breakfast cereals 10 ppm
Hard candy 50 ppm
2,3-Pentanedione is also utilized as a starting material in the synthesis of various chemicals .
Health and Safety Considerations:
Exposure to 2,3-pentanedione has been associated with respiratory health concerns. Studies indicate that inhalation can lead to severe respiratory tract injury, including fibrosis and necrosis, similar to the effects observed with diacetyl exposure. Animal studies have shown that it can cause genetic changes in the brain and alter gene expression. Due to its potential pulmonary toxicity, there is concern regarding its use as a flavoring agent, particularly in occupational settings where inhalation exposure may occur.
2,3 Pentane dione synthesis
pentanedione can be synthesized starting from various products as outlined below .
The simplest route is the one starting from carbohydrates which give lactic acid by fermentation with a lactobacillus strain (chemical yield >95%) .The lactic acid reacts on itself with various catalyst (temperature range 200/350°c) to give 2,3 pentanone dione , the product being purified by distillation .This route is examplified in several patents (example US5731471.) or academic publications (one of the last one ) which are dealing about the best catalyst to run the reaction .
C6H12O6 ===================> 2 CH3CHOHCO2H
2 CH3CHOHCO2H =============>2,3 pentane dione + CO2 + 2 H2O
Another simple way to get 2,3 pentanone dione is starting from glycerol , a by product widely available from the biofuel industry ,by dehydration to get hydroxy aceton which is formylated to obtanin 2,3pentane dione .This route is covered by numerous patents
The third route is starting from pentene 2 to get 2,3 pentandiol (either by classical route HClO/Ca(OH)2/H2O or oxydataion+hydration) .The 2,3 petanediol is oxydized in 2,3 pentanedione using silver catalyst ,It should be noted that 2,3 pentanediol can also be dehydrogenetated in vapor phase using ZnO or Cu catalyst to give 2,3 pentandione .
2,3 pentandiol can be also oxydized by the iodo oxybenzoic acid (KBrO3+ 2 iodobenzoic acid ) to give 2,3 pentane dione , this route being patented in 1993
Some other synthesis are also possible for example by oxydation of 2 pentanone (first mentioned in 1888) or hydroxy pentanone (patented by several corporation)
more details here
