rev 16/1/25
Salicylaldehyde
Salicylaldehyde (SA) (C6H4CHO-2-OH) is a useful
aromatic organic chemical. It is a common reactant for many synthesis,
such as cyclic organic compounds like coumarin and organic ligand such
as salen ligand (2 moles of SA + 1 mole of ethylene diamine) The easy synthesis and modifications of the salen ligand framework
made it the platform of choice for the discovery of new catalysts and
reactions.
Salicylaldehyde is
widely used in the production of agricultural chemicals, medicine,
integrated agent; The salicylic aldehyde in low concentration has the
ability of very strong antibacterial activity (example here) ;
As an oxidation inhibitor it can be used in Plastic Resin industry;. It is widely used
in for the synthesis of tonka bean camphor in fragrance industry in
soap, washing composition, compound perfume, candy and tobacco
industry;
It
also serves as a chelating agent with heavy metal ions such as
Copper(II) ion, which is applicable to colorimetric analysis of the
concentration of heavy metal ions in water sample.
As a chemical
intermediate Salicylaldehyde is very often used (some examples here)
Salicylic
aldehyde can form sequestrant with various metals ,propertie used by
the electroplating industry where salicylic aldehyde is used as a
kind of brightener
and levelling agent; In the oil industry, many affixtures of salicylic
aldehyde can improve the high-temperature stability of oil fuel,
gasoline or petrol.; Salicylic aldehyde and derivative thereof are
the raw materials of coumarin, indoline, benzo pyran organic
photosensitive
material, and can synthesize durable hair-setting agent.
Natural
salicylic aldehyde is mainly present in isolated volatile oil, can not
meet human wants far away from embroidery suede chrysanthemum shaddock
plant.
This is a very short list of salicylaldehyde usage ,if you ask for the keyword salicylaldehyde
in title or abstract of GOOGLE PATENT you will get hundreds of
applications for salicylaldehyde in the real world .
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
SALICYLALDEHYDE
Molecular Formula C7 H6 O2 Synonyms - SALICYLALDEHYDE
- 2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
- 90-02-8
- o-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
- o-Formylphenol
Molecular Weight 122.12 g/mol pKa 6.8 Specific gravity 1.17 gr/cm3 Ebullition 197°c /760 torr Melting point -7°c Azeotrope with water : Eb=98.4°c ( 20% of salicyladehyde 80% water) Refractive Index : 1.5740 at 20 °C/D Solubility slightly soluble in water; soluble in organic solvents, oils
Taste Nut-like, coumarin flavor at low levels
Used in perfumes, flavoring agents, Reported uses : 1 to 10 ppm)
Occurs naturally in cassia oil; [Ullmann] | 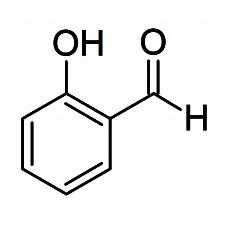 |
Salicyl alcohol
Synonyms - salicyl alcohol
- 2-HYDROXYBENZYL ALCOHOL
- 90-01-7
- 2-(Hydroxymethyl)phenol
- Saligenin
Molecular Weight 124.14 g/mol
Specific gravity 1.16 gr/cm3
Melting point 86°c
Boiling point 267°c /760 Torr | 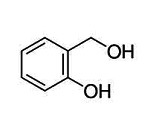 |
2 SALICYLALDEHYDE PRODUCTION
Salicyladehyde can be made from commercially available products following different routes :
*2-1 PHENOL/FORMOL processes
*2-2 PHENOL/CHCl3 process (Reimer Tiemann)
*2-3 ORTHOCRESOL process
* 2-4 Miscellaneous processes
2-1 FORMOL PROCESSES
The reaction consist of making condensation of formol ,generally in the form of paraformaldehyde ( the polymerized
form of formol with a typical degree of polymerization of 8–100
units ) which is a solid melting point 120°c on phenol often without any
solvent
At least 3 process types with variants :
Borate process ,
Cation process ,
Mg process
Formanek process
2-1-1"Borate" process
EP 0,327,473 (1/2/1988)
Borate/Formol process (EP0667331A1 Rhodia Chimie SAS Worldwide applications 1994
US5,689,009 nov 18, 1997
Phenol
reacts on boric acid to get "borated phenol" which reacts on formol ,
condesation being made on the ortho position with small amount of para
isomer .The borated saligenol is decomposed with sodium hydroxyde to
get the saligenol .Chemical yield in saligenol is over 87% base on
phenol charged the remainder being unreacted phenol and para
isomer (more details here)
.The aqueous solution of saligenol is directly oxydised with pure
oxygen with a suitable catalyst (either Pt/C + additives or others ) to
get salicyladehyde which is isolated by azeotropic distillation
.The overall yield based on phenol charged is around 70%
.The mains drawbacks of this process is to use boric acid
which is not recovered and to give a large amount of phenolic waste
which has to be treated to comply to local regulations .
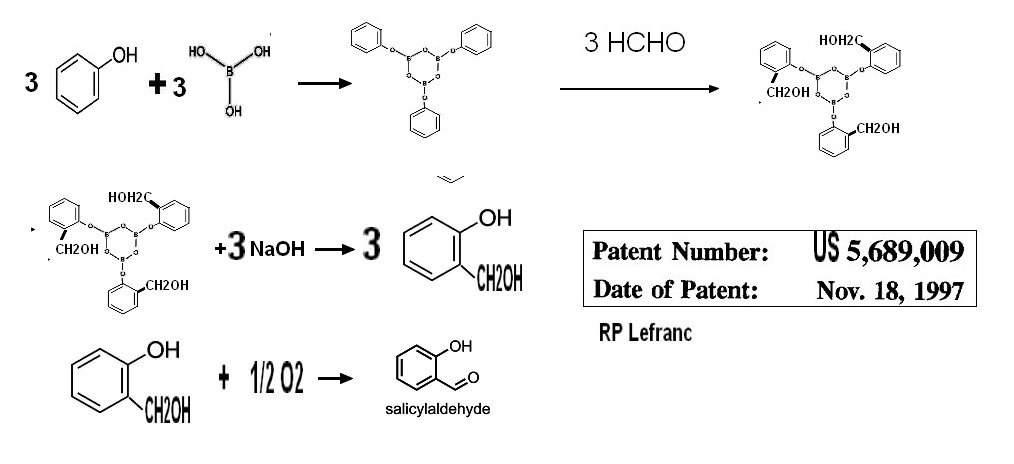
Details on lab procedure
2-1-2"Cation catalyst " process
The
reaction is done by reaction of phenol in excess on formol (for
example 2 moles of phenol/1 mole formol) solvent being Phenol
in
presence of a catalytic amount of a various metal salt (Mono
/di/trivalent like Al,Mg, Cu,Zn,Na...) (typical amount less than 1% on
molar basis compare to formol in the case of homogeneous catalysis ) at
temperature in the 75/85°c
range .By keeping the conversion of phenol under 50% the reaction is
very selective the main by products being the 2,6 diformyl phenol
i and no parahydroxy benzaldehyde It is worth noting that if the
reaction is made not
in anhydrous state but using a formol aqueous solution (37%
formol) the reaction gives a mixture of ortho and para hydroxy
benzaldehyde .Insteadt of using paraformaldehyde ( solid melting
point °c) it is possible to use methanol which is
dehydrogenated into formol vapors on a proprietary catalyst
(microchem proc 943)
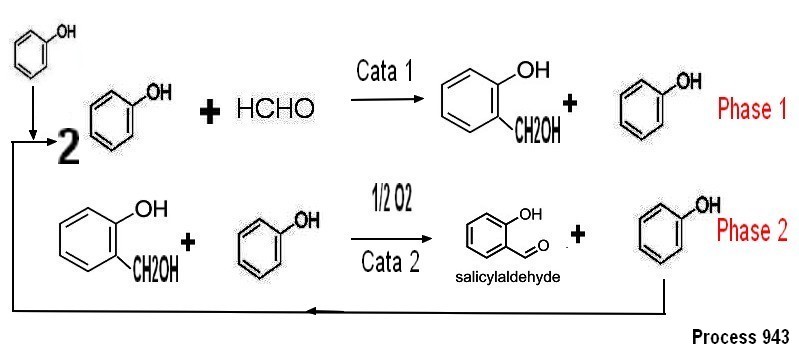
Details on lab procedure to make saligenol
The
oxydation of saligenol to salicylaldehyde can be done directly on the
reaction mixture with oxygen (catalyst Pt/C doped with various
additive like Bismuth to prevent overoxydation to salicylic
acid or
others catalytical systems without any noble metal catalyst such as
copper, nickel, cobalt, iron and manganese.) .It should be noted that
the catalytical system used in phase 1 can be the same as the one of
phase 2 .After oxydation the reaction mixture is distillated
to recover salicylaldehyde (azeotropic distillation) , the phenol
in excess
being extracted and recoverd by vaccum distillation
so as to be recycled . The process
generate a mixture of by products mostly 2,4 and 2,6
diformyl phenol .The
chemical yield for salicylaldehyde on phenol consumed is more than
70% It is a one
pot synthesis in the case of using supported catalyst for
condensation/oxydation .On top of this the process does not
generate any phenolic aqueous waste .
example of lab procedure oxidation with Co chelate here
References of some relevant patents:
*US4026950A
(1975) Inventor Joel Le LudecCurrent
Assignee Rhone Poulenc Industries SA (oxydation
cat Pt/Pd + Bi).
*DE2915216A1 (1979) (Harmann Reimer phenol/formol soude OHB+ PHB
*Process 943 Microchem.fr
*US4460799A (1981) Current Assignee Saint Gobain Isover (cata cond.Al)
*CN1045095A 1989 Process for preparing salicylal from salicylcohol by catalytic oxidation of non-noble metal complex
*EP0069016B1 1985-09-18
Rhone Poulenc (catalyst .Al salt)
*CN
89105025 1989-02-24 catalytic oxidation of salicyl alcohol with non-noble metal complex
Current Assignee Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS
*US8431750B2; 2008-06-03 Application filed by Rhodia Operations SAS oxidation catalyst
Formol production info
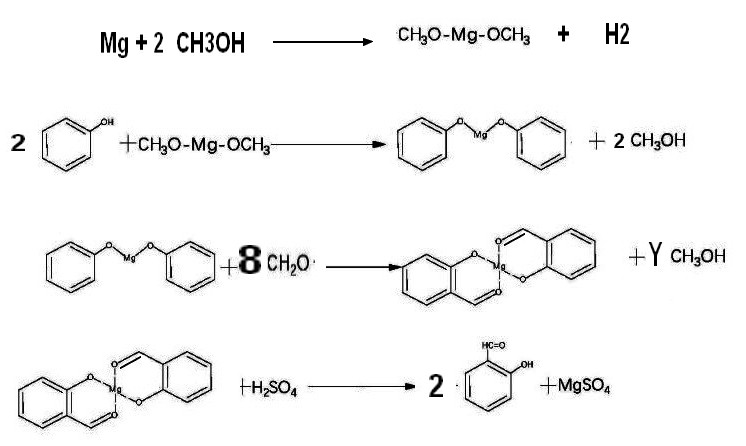
2-1-3"Magnesium" process
CN117164444A
* 2023-09-01 Synthesis method of
salicylaldehyde Current Assignee Zhejiang
Hongda Chemicals Co ltd
CN105669414A 2015-12-09 ,CN117164444A 2023-09-01
The
process use magnesium to get phenol/Mg salt (by reaction of
magnesium methylte on phenol solvent methanol) .The magnesium phenate
reacts with a large
exess of paraformaldehyde (4 times theoritical amount ) to give after
acidification salicylaldehyde .The chemical yiled base on phenol
is in the 80% range .The main drawbacks is the consumption of
Magnesium in stoechiometric amount and the huge amount of
paraformaldehyde
specific consumption for 1 kg of salicyladehyde :Mg=0.17 Kg, Phenol=0.96 kg, Formol=1.07 kg ,H2SO4 100% =0.8 kg
Details on lab procedure
2-1-4 Formanek process
FR2514344A1 1981-10-09 Application filed by Rhone Poulenc
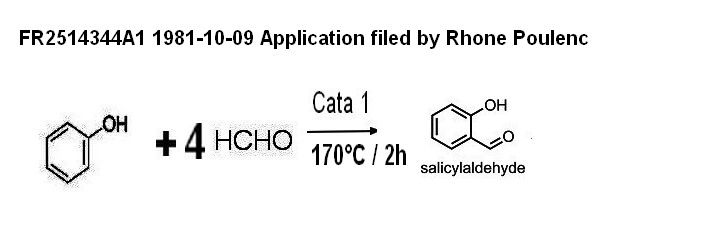
condesation
of phenol on an excess of formol with a catalyst giving
directly salicyl aldehyde (chemical yield 74% on phenol consummed )
proof of concept experiment
2-2 "Reimer Tiemann" process
Traditional
Reimer-Tiemann method ( Reimer K. Tiemann F Ber.,1876,9,824,1285 and Chem.Review.1960, (60): 1969-1984), take phenol
as raw material in alkaline medium. Phenol is ionized into sodium phenate, and chloroform generates diclorocarben
in this basic media .By reaction on phenate , dichlorocarben first forms
benzyl chloride which is hydrolyzed into aldehyde
through acidification, .The salicylic aldehyde generated is
recovered through azeotropic distillation with water .
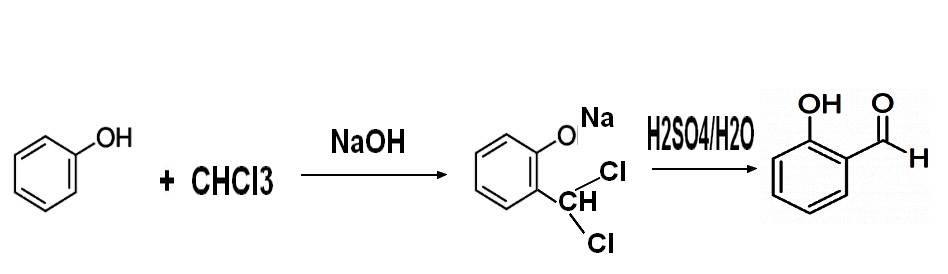
This
method is
simple to operate, and raw material are easy to get, but reaction
yield
is in the 50% range based on phenol and even lower on chloroform,
and quantity of alkali consumption is large as the amount of
phenolic wastewater to dipose off. Chloroform is not an expansive product .It is
obtained by chlorination of methane which gives a mixture methyl chloride methylene chloride cholroformes and carbon
tetrachloride ,all these products having an active market .as chemical intermediates or solvents .
This
synthesis is covered by several patents showing how to improve
the yield and selectivity on salicylaldehyde (refer to reference
list)
Although
Reimer-Tiemann method improvement plans emerge
in an endless stream over the years , as for example using used methyl
alcohol (US3365500) or glycol or other solvvant as reaction
medium the chemical yield remains modest in the 60% range .
Some patents references :
US3365500A Hydroxybenzaldehyde process 1964 Current Assignee Dow Chemical Co
US4324922A
* 1979-06-28 1982-04-13 The Dow Chemical
Company Reimer-Tiemann aldehyde synthesis process
US4469894A
* 1981-06-16 1984-09-04 Sumitomo Chemical Co.,
Ltd. Process for preparation of hydroxybenzaldehydes
US4755613A * 1985-07-10 1988-07-05 Institut National Polytechnique
Details on lab procedure for Riemer process (example from beta naphtol) ,lab procedure DOW ,
Chloroform
which can be produced by reaction of chlorine on methane has a large market
.It is a main intermediate for various chemicals as R-22
and PTFE , more details here on its production .
2-3"Ortho cresol" process
Chlorination + hydrolyse
US1023758A Inventor Friedrich Raschig (1909)
US3314998A (1964) Universal Oil Products C
US3641158A Current Assignee Evonik Corp (1969)
US4490559A * 1984-03-27 1984-12-25 Shell Oil Company Process for making aldehydes from diesters of carbonic acid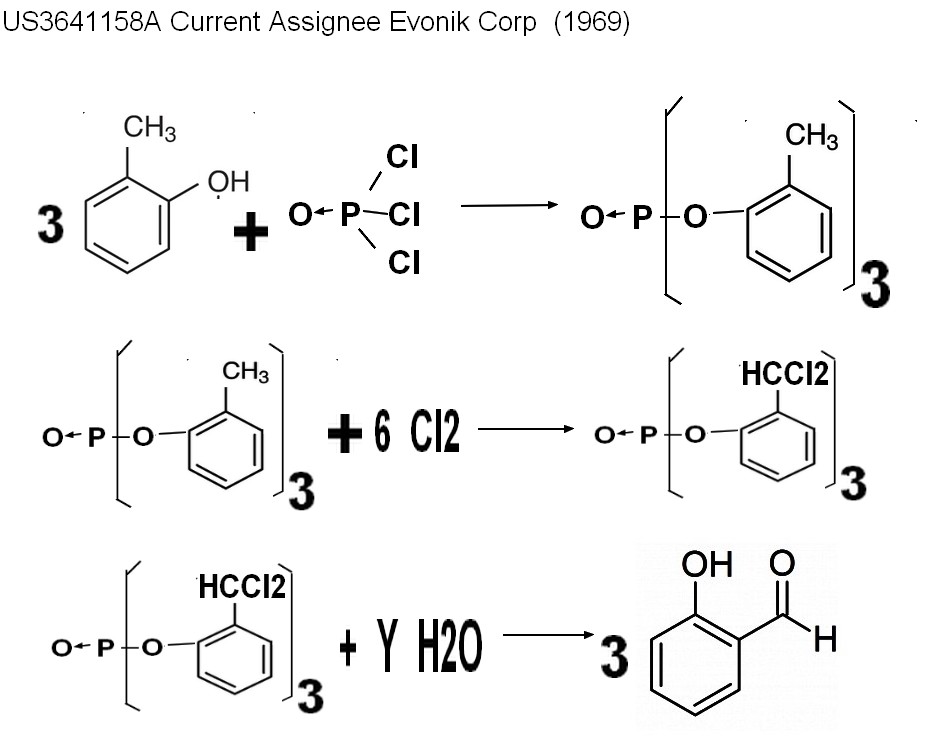
Example of lab procedureDirect oxydation Industrial chemistry Library vol 8 p 388 (Elsevier)
US5354919(1992)
CA2099681A1·1993-12-30
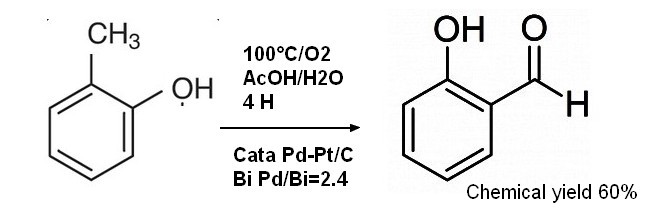 2-4 Miscellaneous processes
2-4 Miscellaneous processes "Ozonolyse process"
DE4104835A1 (1991) BASF SE Salicylaldehyde prodn. - by ozonisation of o-propenyl-phenol
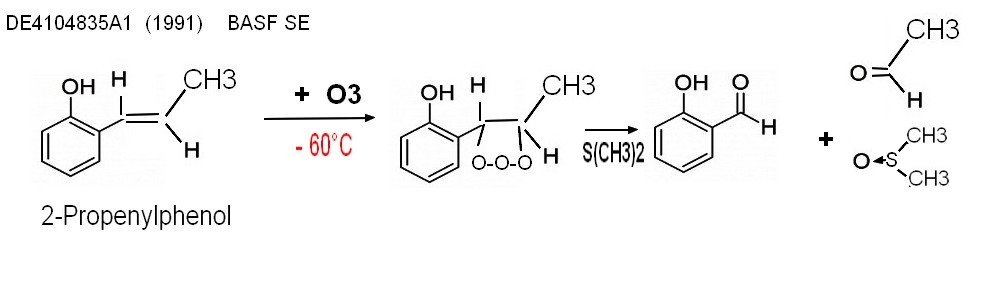
lab procedure
"ELECTRO reduction of salicylic acid "
CN101008086A (2006) Current Assignee East China University of Science and Technology
The invention relates to a direct electro-reduction method for preparing
ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid in H type
electrolyser, which is characterized in that quaternary ammonium salt
addictive is added in cat electrode room. It takes lead plate as cathode
and anode, takes ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde and hydric sulphate as
electrolytic solution for cathode and anode, the current efficiency
reach over 35% at 10- 40 Deg. C and current density of 500- 2000 A/ m2,
which is 10% more than that without additive. 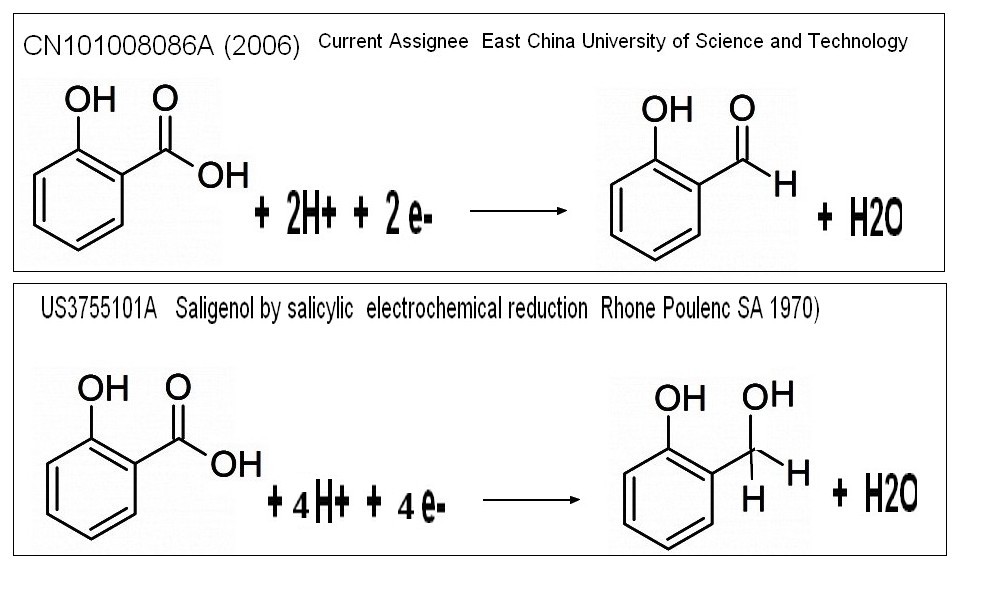
As
is the process giving salicylaldehyde cannot compete with chemical processes The main
problem is to prevent further reduction of salicylaldehyde produced
into saligenol .
An older patent claimed more decent chemical yield in saligenol starting from salicylic acid (US3755101A Rhone Poulenc SA 1970)CN101008086 : Lab procedure example
Electro reduction to saligenol : lab procedure
OTHER WELL KNOW PROCESSES to get Hydroxy aldehyde from phenol
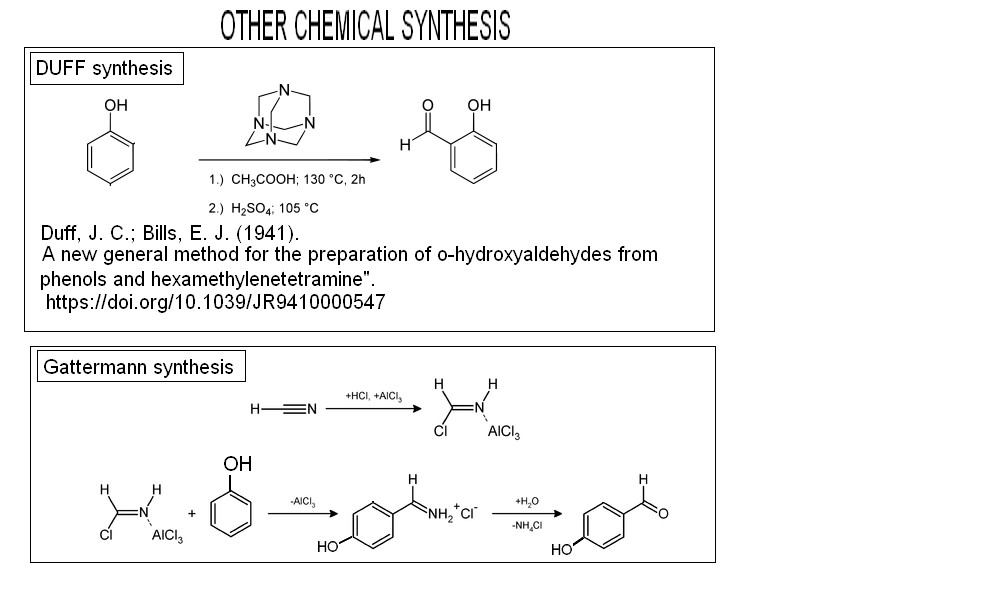
***************************************************
More details related to salicylaldhyde patents
More details related to saligenol patents













